Stationary Recycling Crusher Plants for Slag
Slag, a byproduct of metal smelting processes, is produced in large quantities by steel mills, foundries, and other metalworking industries. While once considered waste, slag is now recognized as a valuable resource due to its potential applications in construction, road building, and other industries. Stationary recycling crusher plants for slag play a crucial role in converting this industrial byproduct into useful materials, driving sustainability and reducing environmental impact. This article explores the importance, functionality, and advantages of stationary recycling crusher plants for slag.
What is Slag?
Slag is a stony byproduct left over after the extraction of metal from its ore. It typically contains a mixture of metal oxides and silicates, along with small amounts of metal residues. Depending on the metal production process (such as iron, steel, or copper smelting), the composition of slag may vary. For example, blast furnace slag (from iron production) contains calcium, magnesium, aluminum, and silicon oxides, making it highly versatile for further use.
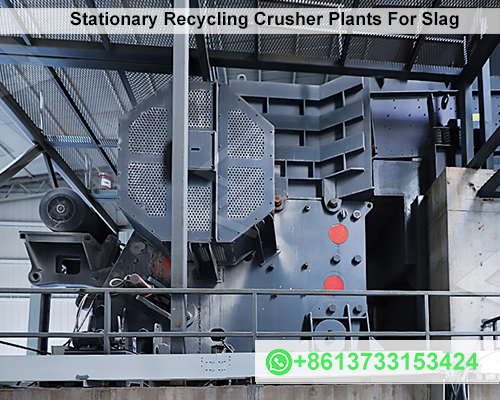
The Role of Stationary Recycling Crusher Plants
Stationary recycling crusher plants are large-scale, immobile systems designed to crush and process slag into finer particles for reuse in different industries. These plants are typically located near industrial facilities, allowing for the efficient recycling of slag without the need for long transportation. The main objective of these plants is to break down slag into smaller sizes that can be used as aggregates for road construction, cement production, and other applications.
How Stationary Recycling Crusher Plants Work
- Primary Crushing: The first stage in the process involves feeding large pieces of slag into a jaw crusher or impact crusher. This machine reduces the size of the material to manageable pieces.
- Secondary Crushing: After the initial crushing, the material is transferred to a secondary crusher (cone crusher or impact crusher), where it is further reduced to smaller, uniform particles.
- Screening and Sorting: The crushed slag is then screened to separate it based on size and quality. Some plants include magnetic separation to remove any remaining metal content.
- Final Processing: The finer slag particles are processed, sorted, and stored, ready to be reused in various applications. High-quality aggregates may be further refined or mixed with other materials to enhance their properties.
Advantages of Stationary Recycling Crusher Plants for Slag
- Environmental Benefits: Recycling slag significantly reduces the amount of waste that ends up in landfills. The process prevents the need for additional mining of raw materials, conserving natural resources and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Cost-Effective: Using recycled slag as an aggregate material is often cheaper than sourcing virgin materials. It can also help reduce the disposal costs for industries that generate large amounts of slag.
- Sustainability: By converting industrial waste into valuable resources, stationary recycling crusher plants contribute to a more sustainable circular economy, where waste materials are repurposed rather than discarded.
- Improved Product Quality: Crushed slag can improve the properties of construction materials. For instance, when used in road base layers, it enhances durability and resistance to weathering. In cement production, slag helps reduce energy consumption and improves the strength of concrete.
Key Considerations for Stationary Recycling Crusher Plants
- Plant Size and Capacity: The size and capacity of the plant must align with the volume of slag being produced by the industry. High-capacity plants are essential for facilities that generate significant amounts of slag daily.
- Crushing Technology: Choosing the right type of crusher (e.g., jaw, impact, cone) depends on the specific characteristics of the slag being processed. Some types of slag may require a combination of crusher for effective processing.
- Maintenance and Longevity: Since slag can be abrasive, crusher plants must be designed with durable materials that can withstand heavy wear and tear. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure consistent performance.
- Automation and Efficiency: Many modern stationary recycling crusher plants incorporate advanced automation systems that optimize energy usage, reduce operational costs, and minimize manual labor.
Applications of Recycled Slag
- Construction Aggregates: Recycled slag is widely used as a substitute for gravel or crushed stone in construction. Its strength and durability make it ideal for road bases, asphalt, and concrete.
- Cement Production: Slag can be ground into a fine powder and used as a supplementary cementitious material (SCM) in concrete production. This improves the strength and durability of the concrete while reducing the need for Portland cement.
- Soil Improvement: Ground slag can also be used to enhance soil quality in agriculture or landscaping, particularly in areas with acidic soils, as it acts as a natural soil conditioner.
- Metal Recovery: Some stationary crusher plants are equipped with magnetic separators to recover residual metal from slag, further increasing the value of the recycled material.
Stationary recycling crusher plants for slag are an essential part of the modern recycling infrastructure. By transforming industrial waste into reusable materials, these plants help reduce the environmental impact of slag disposal while contributing to more sustainable construction practices. As industries continue to focus on reducing waste and conserving resources, the role of these crusher plants will only become more significant in the future.
Through innovation, sustainability, and efficiency, stationary recycling crusher plants help close the loop on industrial waste management, ensuring that slag, once viewed as a byproduct, can now be recognized as a valuable resource for the global economy.









